動(dòng)畫的原理是在一個(gè)時(shí)間段內(nèi),多次改變UI外觀,由于人眼會(huì)產(chǎn)生視覺暫留,所以最終看到的就是一個(gè)“連續(xù)”的動(dòng)畫。UI的一次改變稱為一個(gè)動(dòng)畫幀,對應(yīng)一次屏幕刷新,而決定動(dòng)畫流暢度的一個(gè)重要指標(biāo)就是幀率FPS(Frame Per Second),即每秒的動(dòng)畫幀數(shù),幀率越高則動(dòng)畫就會(huì)越流暢。
ArkUI中,產(chǎn)生動(dòng)畫的方式是改變屬性值且指定動(dòng)畫參數(shù)。動(dòng)畫參數(shù)包含了如動(dòng)畫時(shí)長、變化規(guī)律(即曲線)等參數(shù)。當(dāng)屬性值發(fā)生變化后,按照動(dòng)畫參數(shù),從原來的狀態(tài)過渡到新的狀態(tài),即形成一個(gè)動(dòng)畫。
ArkUI提供的動(dòng)畫能力按照頁面的分類方式,可分為頁面內(nèi)的動(dòng)畫和頁面間的動(dòng)畫。如下圖所示,頁面內(nèi)的動(dòng)畫指在一個(gè)頁面內(nèi)即可發(fā)生的動(dòng)畫,頁面間的動(dòng)畫指兩個(gè)頁面跳轉(zhuǎn)時(shí)才會(huì)發(fā)生的動(dòng)畫。
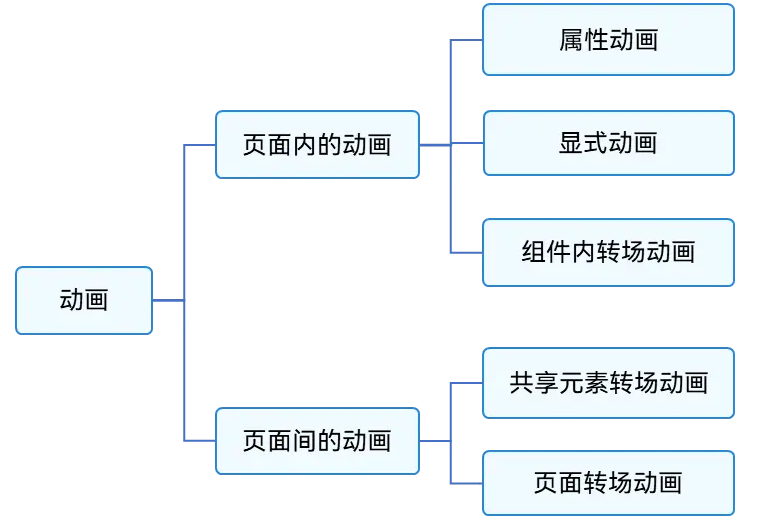
圖1 按照頁面分類的動(dòng)畫
如果按照基礎(chǔ)能力分,可分為屬性動(dòng)畫、顯式動(dòng)畫、轉(zhuǎn)場動(dòng)畫三部分。如下圖所示。
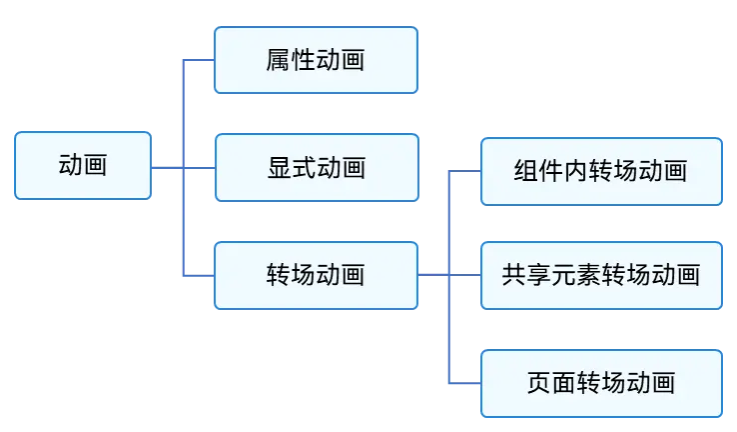
圖2 按照基礎(chǔ)能力分類的動(dòng)畫
使用顯式動(dòng)畫產(chǎn)生布局更新動(dòng)畫
顯式動(dòng)畫的接口為:
animateTo(value: AnimateParam, event: () => void): void
第一個(gè)參數(shù)指定動(dòng)畫參數(shù),第二個(gè)參數(shù)為動(dòng)畫的閉包函數(shù)。
以下是使用顯式動(dòng)畫產(chǎn)生布局更新動(dòng)畫的示例。示例中,當(dāng)Column組件的alignItems屬性改變后,其子組件的布局位置結(jié)果發(fā)生變化。只要該屬性是在animateTo的閉包函數(shù)中修改的,那么由其引起的所有變化都會(huì)按照animateTo的動(dòng)畫參數(shù)執(zhí)行動(dòng)畫過渡到終點(diǎn)值。
@Entry
@Component
struct LayoutChange {
// 用于控制Column的alignItems屬性
@State itemAlign: HorizontalAlign = HorizontalAlign.Start;
allAlign: HorizontalAlign[] = [HorizontalAlign.Start, HorizontalAlign.Center, HorizontalAlign.End];
alignIndex: number = 0;
build() {
Column() {
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Button("1").width(100).height(50)
Button("2").width(100).height(50)
Button("3").width(100).height(50)
}
.margin(20)
.alignItems(this.itemAlign)
.borderWidth(2)
.width("90%")
.height(200)
Button("click").onClick(() => {
// 動(dòng)畫時(shí)長為1000ms,曲線為EaseInOut
animateTo({ duration: 1000, curve: Curve.EaseInOut }, () => {
this.alignIndex = (this.alignIndex + 1) % this.allAlign.length;
// 在閉包函數(shù)中修改this.itemAlign參數(shù),使Column容器內(nèi)部孩子的布局方式變化,使用動(dòng)畫過渡到新位置
this.itemAlign = this.allAlign[this.alignIndex];
});
})
}
.width("100%")
.height("100%")
}
}
除直接改變布局方式外,也可直接修改組件的寬、高、位置。
@Entry
@Component
struct LayoutChange2 {
@State myWidth: number = 100;
@State myHeight: number = 50;
// 標(biāo)志位,true和false分別對應(yīng)一組myWidth、myHeight值
@State flag: boolean = false;
build() {
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Button("text")
.type(ButtonType.Normal)
.width(this.myWidth)
.height(this.myHeight)
.margin(20)
Button("area: click me")
.fontSize(12)
.margin(20)
.onClick(() => {
animateTo({ duration: 1000, curve: Curve.Ease }, () => {
// 動(dòng)畫閉包中根據(jù)標(biāo)志位改變控制第一個(gè)Button寬高的狀態(tài)變量,使第一個(gè)Button做寬高動(dòng)畫
if (this.flag) {
this.myWidth = 100;
this.myHeight = 50;
} else {
this.myWidth = 200;
this.myHeight = 100;
}
this.flag = !this.flag;
});
})
}
.width("100%")
.height("100%")
}
}
另一種方式是給第二個(gè)Button添加布局約束,如position的位置約束,使其位置不被第一個(gè)Button的寬高影響。核心代碼如下:
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Button("text")
.type(ButtonType.Normal)
.width(this.myWidth)
.height(this.myHeight)
.margin(20)
Button("area: click me")
.fontSize(12)
// 配置position屬性固定,使自己的布局位置不被第一個(gè)Button的寬高影響
.position({ x: "30%", y: 200 })
.onClick(() => {
animateTo({ duration: 1000, curve: Curve.Ease }, () => {
// 動(dòng)畫閉包中根據(jù)標(biāo)志位改變控制第一個(gè)Button寬高的狀態(tài)變量,使第一個(gè)Button做寬高動(dòng)畫
if (this.flag) {
this.myWidth = 100;
this.myHeight = 50;
} else {
this.myWidth = 200;
this.myHeight = 100;
}
this.flag = !this.flag;
});
})
}
.width("100%")
.height("100%")
使用屬性動(dòng)畫產(chǎn)生布局更新動(dòng)畫
顯式動(dòng)畫把要執(zhí)行動(dòng)畫的屬性的修改放在閉包函數(shù)中觸發(fā)動(dòng)畫,而屬性動(dòng)畫則無需使用閉包,把a(bǔ)nimation屬性加在要做屬性動(dòng)畫的組件的屬性后即可。
屬性動(dòng)畫的接口為:
animation(value: AnimateParam)
其入?yún)閯?dòng)畫參數(shù)。想要組件隨某個(gè)屬性值的變化而產(chǎn)生動(dòng)畫,此屬性需要加在animation屬性之前。有的屬性變化不希望通過animation產(chǎn)生屬性動(dòng)畫,可以放在animation之后。上面顯式動(dòng)畫的示例很容易改為用屬性動(dòng)畫實(shí)現(xiàn)。例如:
@Entry
@Component
struct LayoutChange2 {
@State myWidth: number = 100;
@State myHeight: number = 50;
@State flag: boolean = false;
@State myColor: Color = Color.Blue;
build() {
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Button("text")
.type(ButtonType.Normal)
.width(this.myWidth)
.height(this.myHeight)
// animation只對其上面的type、width、height屬性生效,時(shí)長為1000ms,曲線為Ease
.animation({ duration: 1000, curve: Curve.Ease })
// animation對下面的backgroundColor、margin屬性不生效
.backgroundColor(this.myColor)
.margin(20)
Button("area: click me")
.fontSize(12)
.onClick(() => {
// 改變屬性值,配置了屬性動(dòng)畫的屬性會(huì)進(jìn)行動(dòng)畫過渡
if (this.flag) {
this.myWidth = 100;
this.myHeight = 50;
this.myColor = Color.Blue;
} else {
this.myWidth = 200;
this.myHeight = 100;
this.myColor = Color.Pink;
}
this.flag = !this.flag;
})
}
}
}
上述示例中,第一個(gè)button上的animation屬性,只對寫在animation之前的type、width、height屬性生效,而對寫在animation之后的backgroundColor、margin屬性無效。運(yùn)行結(jié)果是width、height屬性會(huì)按照animation的動(dòng)畫參數(shù)執(zhí)行動(dòng)畫,而backgroundColor會(huì)直接跳變,不會(huì)產(chǎn)生動(dòng)畫
審核編輯 黃宇
-
鴻蒙
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
57文章
2392瀏覽量
43050
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
【書籍評測活動(dòng)NO.56】極速探索HarmonyOS NEXT:純血鴻蒙應(yīng)用開發(fā)實(shí)踐
鴻蒙機(jī)器人與鴻蒙開發(fā)板聯(lián)動(dòng)演示
鴻蒙Flutter實(shí)戰(zhàn):07混合開發(fā)
鴻蒙OpenHarmony南向/北向快速開發(fā)教程-迅為RK3568開發(fā)板
哪吒汽車APP啟動(dòng)鴻蒙原生應(yīng)用開發(fā)
鴻蒙開發(fā)就業(yè)前景到底怎么樣?
HarmonyOS開發(fā)案例:【轉(zhuǎn)場動(dòng)畫】

OpenHarmony實(shí)戰(zhàn)開發(fā)-如何實(shí)現(xiàn)動(dòng)畫幀
鴻蒙OS崛起,鴻蒙應(yīng)用開發(fā)工程師成市場新寵
OpenHarmony實(shí)戰(zhàn)開發(fā)-如何實(shí)現(xiàn)組件動(dòng)畫。
鴻蒙OS開發(fā)學(xué)習(xí):【尺寸適配實(shí)現(xiàn)】




 鴻蒙開發(fā)之發(fā)動(dòng)畫篇
鴻蒙開發(fā)之發(fā)動(dòng)畫篇











評論